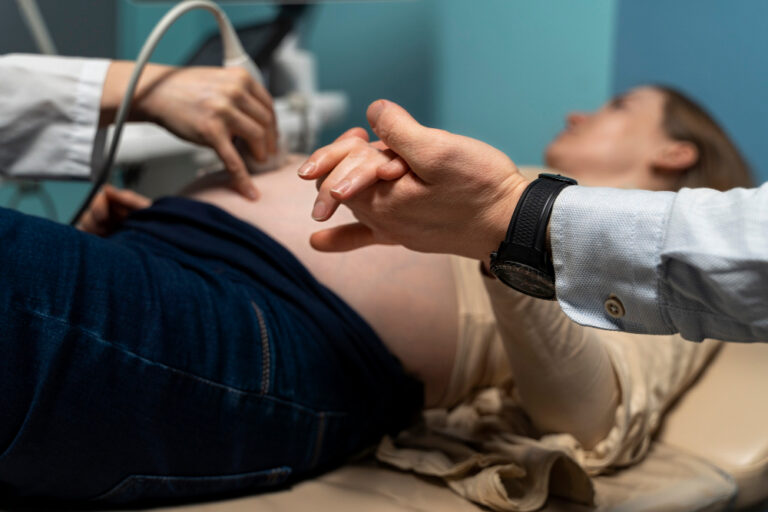
High Risk Pregnancy
- Home
- Treatments Offered
- High Risk Pregnancy
Dr. Smita Jadhav: High-Risk Pregnancy Doctor in Salt Lake
What is a high-risk pregnancy?

When does a pregnancy become high-risk?
- Is 17 years old or younger
- Is 35 years old or older
- Was underweight or overweight before pregnancy
- Is expecting twins, triplets, or other multiples
- Has high blood pressure, diabetes, depression, or other health conditions
- Has experienced complications in a previous pregnancy, such as premature labor or having a child with a genetic condition or birth defect

What is Abnormal Menstruation?
Abnormal menstruation, or menstrual irregularity, refers to any deviation from a regular menstrual cycle. While variations in menstrual patterns are common, abnormal menstruation involves significant deviations in frequency, duration, or intensity. This condition can manifest in various ways, disrupting the usual rhythm of a woman’s menstrual cycle and, in some cases, leading to other, more severe health concerns.
Send Us Message
Call Us
+91 9748825624
Email Us
drsmitajadhav76@gmail.com
Our Location
IB-193, Broadway Rd, IB Block, Sector III, Bidhannagar, Kolkata, West Bengal 700106
Tips to manage a high-risk pregnancy

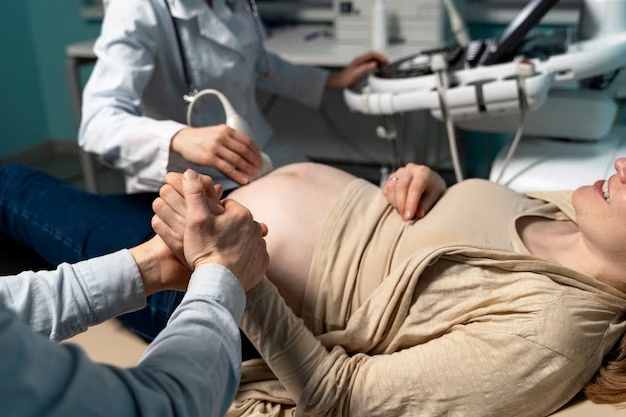
Reduce High-risk Pregnancy Complications
- Schedule a preconception checkup with the doctor
- Educate yourself about your condition
- Attend all prenatal appointments
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, gain appropriate weight, and stay active if possible

What is Abnormal Menstruation?
Abnormal menstruation, or menstrual irregularity, refers to any deviation from a regular menstrual cycle. While variations in menstrual patterns are common, abnormal menstruation involves significant deviations in frequency, duration, or intensity. This condition can manifest in various ways, disrupting the usual rhythm of a woman’s menstrual cycle and, in some cases, leading to other, more severe health concerns.
High-risk Pregnancy vs Normal Pregnancy?
| Features | High-risk Pregnancy | Normal Pregnancy |
|---|---|---|
| Hospital Needs | May need delivery at a hospital with specialized facilities. | Can usually be delivered at a standard hospital or birth center. |
| Medication | Often requires specific medications to manage conditions like blood pressure, diabetes, or preterm labor | Minimal or no medication, aside from standard prenatal vitamins |
| Labor and Delivery Options | May have limited options for labor and delivery | Usually more flexible with options for natural birth, water birth, etc. |
| Genetic Testing | More likely to involve genetic counseling and testing if fetal abnormalities are suspected | May not require genetic testing unless there is a family history |
| Lifestyle Adjustments | Requires stricter adherence to specific guidelines like bed rest or restricted travel | Normal pregnancy adjustments with general precautions |
| Support from Specialists | May involve multiple specialists (cardiologist, endocrinologist, etc.) depending on health conditions | Managed usually by the OB/GYN with minimal specialist interventions |
Treatment for a high-risk pregnancy
- Medication to control pre-existing conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or infections.
- Regular monitoring of the mother and baby with ultrasounds, blood tests, or other diagnostic tests.
- Bed rest or reduced physical activity to avoid preterm labor.
- Nutritional counseling to manage weight and improve overall health.
- Early or scheduled delivery, including possible C-section, if complications arise.