Abnormal Menstruation
- Home
- Treatments Offered
- Abnormal Menstruation
Dr. Smita Jadhav: Best Abnormal Menstruation Treatment in Kolkata
What is Abnormal Menstruation?
Abnormal menstruation, also known as irregular periods, refers to any variation in your menstrual cycle that differs from your regular pattern. This can manifest as changes in the duration, frequency, or flow of your period. For example, if your periods occur less than 21 days apart or more than 35 days apart, this is considered an irregular cycle. Other signs of abnormal menstruation include periods that are longer or shorter than usual, missed periods, or unusually heavy or light bleeding. Understanding what constitutes a typical menstrual cycle is crucial to identifying when something is off and seeking appropriate medical advice if necessary.
Symptoms of Abnormal Menstruation
Here are some symptoms of abnormal menstruation:
- Menstrual cycles occur less than 21 days apart or more than 35 days apart.
- Missing three or more periods in a row.
- Menstrual flow that is significantly heavier or lighter than usual.
- Periods lasting longer than seven days.
- Variability in the length of cycles by more than nine days, such as one cycle being 28 days, the next 37 days, and the following 29 days.
- Severe pain, cramping, nausea, or vomiting accompanying periods.
- Bleeding or spotting between periods, after menopause, or following sexual intercourse.
- Soaking through one or more sanitary pads within an hour.
Contact Dr. Smita Jadhav, the best abnormal menstruation doctor in Kolkata, if you experience any of the aforementioned signs of abnormal menstruation.

What is Abnormal Menstruation?
Abnormal menstruation, or menstrual irregularity, refers to any deviation from a regular menstrual cycle. While variations in menstrual patterns are common, abnormal menstruation involves significant deviations in frequency, duration, or intensity. This condition can manifest in various ways, disrupting the usual rhythm of a woman’s menstrual cycle and, in some cases, leading to other, more severe health concerns.
Causes of Abnormal Periods
As per Smita Jadhav, the best gynecologist in Kolkata, the causes of abnormal menstruation are listed below.

Send Us Message
Call Us
+91 9748825624
Email Us
drsmitajadhav76@gmail.com
Our Location
IB-193, Broadway Rd, IB Block, Sector III, Bidhannagar, Kolkata, West Bengal 700106
Types of Abnormal Menstruation
Types of Abnormal Menstruation are as follows:
1. Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea is characterized by the absence of menstrual periods and occurs when a woman misses more than three consecutive cycles. It can result from various medical conditions, such as anatomical abnormalities, eating disorders, thyroid disorders, excessive exercise, or lifestyle choices. Amenorrhea is also normal before puberty, after menopause, and during pregnancy.
Amenorrhea is divided into:
a. Primary Amenorrhea:
Diagnosed when a woman hasn’t had a period by age 16. Common causes include endocrine issues, low body weight, genetic abnormalities, or delayed pituitary gland maturation.
b. Secondary Amenorrhea:
Occurs when a woman with previously regular periods stops menstruating for three months or more. Causes may include stress, illness, weight loss, thyroid issues, or ovarian cysts.
2. Oligomenorrhea
Oligomenorrhea refers to infrequent menstrual periods occurring more than 35 days apart. It’s common in adolescents and those transitioning into perimenopause. Some of the causes can include:
- PCOS
- Androgen-secreting tumors
- Primary ovarian insufficiency
- Hyperthyroidism
- Diabetes
- Eating disorders
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
3. Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea is characterized by severe menstrual cramps and pain, which may extend to the lower back and thighs. It is classified as:
a. Primary Dysmenorrhea:
Painful cramps without underlying disease, often worsened by heavy abnormal bleeding during periods.
b. Secondary Dysmenorrhea:
Pain associated with conditions like uterine fibroids or endometriosis.
4. Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia involves unusually heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, which can interfere with daily activities. It is often accompanied by painful cramps (dysmenorrhea). Common causes include:
- Hormonal imbalances
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Uterine fibroids
- Miscarriage
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic infections
- Tumors and polyps
- Birth control devices like IUDs
5. Metrorrhagia
Metrorrhagia refers to irregular bleeding between regular menstrual periods, also known as breakthrough bleeding.
6. Polymenorrhea
Polymenorrhea is characterized by menstrual periods occurring more frequently than the usual 21–35-day cycle, though the bleeding duration remains normal. Causes may include:
- High estrogen levels
- Stress
- Certain medications
- Polyps or uterine fibroids
- Thyroid issues
- PCOS
7. Hypomenorrhea
Hypomenorrhea involves very light menstrual bleeding lasting less than two days. It is often associated with:
- Hormonal contraceptives
- Low body fat or obesity
- Hormonal imbalances
- Intrauterine adhesions
- Stress and depression
- Intense exercise
8. Hypermenorrhea
Hypermenorrhea is characterized by excessively frequent and heavy abnormal bleeding from the uterus. It is linked to:
- Hormonal disorders
- Liver disease
- Uterine abnormalities
Diagnosis of Abnormal Menstruation
To diagnose irregular periods, the gynecologist will review your menstrual history and medical background, perform a physical exam, including a pelvic exam, and may order additional tests such as:
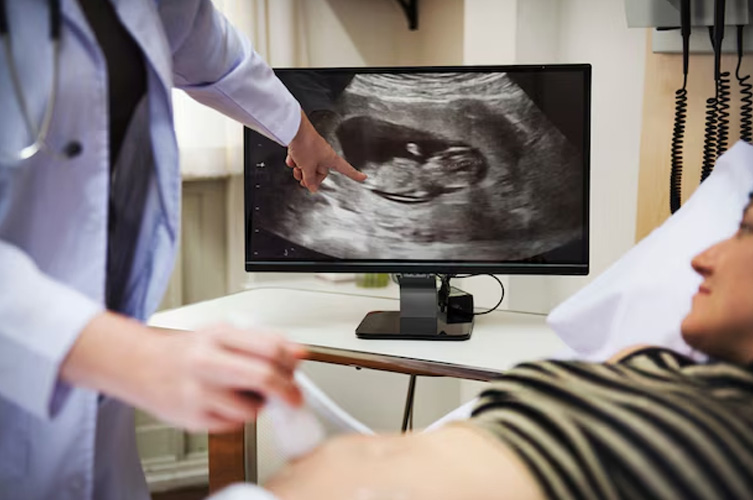
Pelvic Ultrasound
Detects issues like uterine fibroids, polyps, or ovarian cysts.
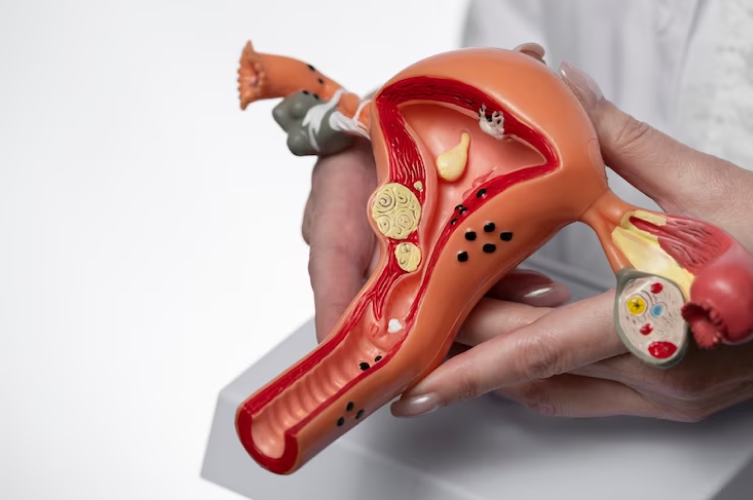
Endometrial Biopsy
Involves taking a tissue sample from the uterus lining to diagnose conditions like endometriosis, hormonal imbalances, or precancerous cells.
Hysteroscopy
Allows the gynecologist to examine the inside of your uterus to diagnose and address abnormal bleeding causes.
Treatments for Abnormal Menstruation
Here are some common treatments for various menstrual issues:
1. Hormonal Therapies
a. Birth Control Pills:
Help regulate periods, reduce heavy bleeding, and manage hormonal imbalances.
b. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT):
Used for symptoms related to perimenopause or menopause.
c. Progestin:
A type of hormone that can help manage irregular bleeding and heavy periods.
2. Lifestyle Changes
a. Diet and Exercise:
Maintaining a healthy weight and regular physical activity can help regulate menstrual cycles.
b. Stress Management:
Techniques like yoga, meditation, and relaxation exercises can alleviate stress-related menstrual irregularities.
3. Medications
NSAIDs:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen can help with pain and heavy bleeding.
4. Surgery
Hysterectomy:
Removal of the uterus, sometimes recommended for severe cases of abnormal bleeding when other treatments have not been effective.
5. Addressing Underlying Conditions:
a. Treating PCOS:
Medications and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms.
b. Managing Thyroid Disorders:
Medications to address thyroid imbalances affecting menstrual cycles.
c. Managing Endometriosis:
Hormonal treatments or surgery to remove endometrial tissue.


